Have you ever heard of an Anchor text? Or Cache? Or an email client?
When you get in to the world of websites for the first time, you will be dealing with website jargon.
That strange glossary may work a bit discouraging, as we don’t use this in our everyday language.
But it is quite useful to keep up a bit with this website jargon
In the following overview I will not only give the descriptions, but I will also wherever possible, add an image to clarify them.
It is already hard enough!
Meet the wonderful world of the website jargon.
Website jargon, the overview:
Above the fold: Above the fold is a term that comes from the newspaper world. This is the part of a website that you see first, which is visible before you go any further. Therefore, this is an important part of the website, that can be decisive whether the visitor stays on your website, or leaves right away.
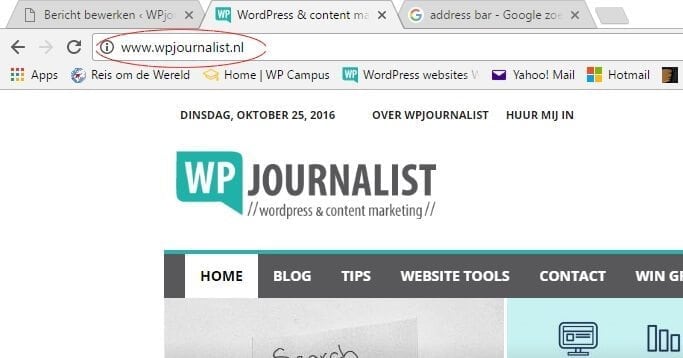
Address bar: This is the white bar on the upper side of the screen, where you can type in the address of a website. Usually this starts with https:// or www.
Anchor text: also known as anchor text. This is the text that becomes visible when you direct a link to another page. If you create a link to the page ‘Which WordPress theme is that?’ for example, then “Which WordPress theme is that” is the anchor text.
ASCII: The abbreviation for American Standard Code for Information Interchange. This is the language of computers and browsers. ASCII-codes make it possible to exchange information from one computer to another (a server for example). To upload information from the computer to the server, you need ASCII or Binary. This depends on the type of file that you upload.
ASP: (Active Server Pages) is meant to design dynamic web pages on the server after a visitor’s request. The technology was developed by Microsoft. Dynamic means that the pages need to be rebuilt each time.
Attribute: An attribute is an element which an object in a database is made out of. An attribute describes an element in the database, such as a chart or a field.
Backlinks: Links from other webpages to your website. Search engines see the amount of backlinks as a sign that your website is valuable. They will put your website higher in the search results accordingly. It is still one of the most important criteria for search engines such as Google.

Backup: Making a copy of a website or file. Backups of your website are often made, in case something goes wrong. For example in case you get hacked or if an update causes your website to no longer be available. In that case you use a backup (essentially an older version of your website that is still good) to recover your website. Often your hosting provider will make backups from your website, but you can also do it yourself through a plugin.
Bandwidth: The amount of space that is available on a connection between the computer and server or servers mutually. You can compare it to a highway. The more lanes on the highway, the more users can go across. That way, websites with lots of visitors need more bandwidth than a website with less visitors.
BCC: This means “Blind Carbon Copy”. It is an e-mail function. If you send a large group of people a BBC email, the email address of the other receivers are not shown in the field ‘to’.
BETA: A term that is used for software that may be ‘live’, but is still in a testing phase. People that use BETA software can expect to still come across a couple of mistakes. A new version of WordPress is in the BETA phase at the start, for example. After this has been extensively tested by all developers, the new version is finally launched.
Binary: A system that consists of two numbers, 0 and 1. Everything that is inserted in a computer, is being transitioned in a unique combination of zero’s and one’s . Computer displays and printers subsequently transfer this into what you typed.
Blog: A returning series of articles in which you share topics or experiences with your readers. Today, blogs are an important marketing tool to connect people with your website, or to tempt them to purchase things.
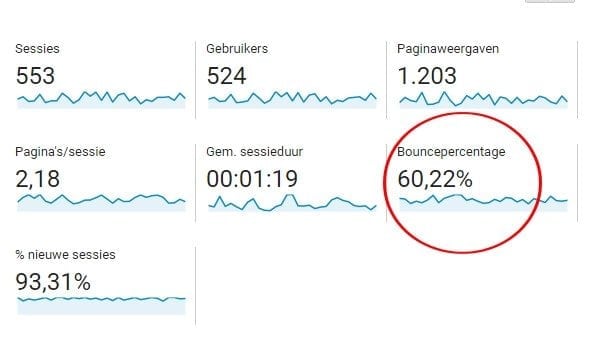
Bounce rate: This is the percentage of visitors that enter a specific page and then click to access another page on the website. This gives a good view of the navigation on a website, but also the quality of the content of a site. A high bounce rate means that visitors leave the site quite quickly. That means there is still a lot of work to do to improve that!
Browser: When you visit a website, you use a browser such as Internet Explorer from Microsoft or Google Chrome.
Cache: Every time you do something on your computer, it is saved in the memory, so that it can be loaded quicker next time. The place where this is all saved, is called ‘cache’. Make sure that your cache is not over-capacitated, as that could slow your computer down quite a bit. In that case, it is important to clear your cache.
For your website, it can be useful to install a cache plugin, which ensures your website loads faster. Two free plugins are W3 Total Cache and WP Super Cache.
CSS or Cascading Style Sheets: This is the code to set the look and feel of a website. CSS has replaced HTML for the layout of websites.
CC: means ‘Carbon Copy’. It is an e-mail function and is used to make a copy of an email and send it to one or more people.
Chat: This is a function with which users from all over the world can communicate in real time. You type something which then appears on the screen of the receiver. Sometimes, you need to install software on both computers, in order to chat with each other. Whatsapp is a chat program, but you can also integrate a chat program into your website.
CMS: Means Content Management System, which is the system with which you can adjust your website. For this, you need to login with your username and password, which will give you access to all sorts of administrator functions in your cms. Here, you can make articles, install plugins and monitor your website.
Code: The internet is nothing other than a collection of codes. There are different sorts of code programming languages that are used to connect websites and all the computer programs and software, such as javascript and php.
Conversion: A marketing term to convert the amount of visitors from a website to buyers. If 1 out of 10 visitors from your website buys something, there is a conversion of 1 out of 10 (10%). Conversion is important, as it may be fun to have thousands of visitors, but if none of them buy a product or service, you still have nothing.
Cookie: A piece of information that websites save on your computer when you visit them. Cookies are usually harmless. Sometimes, they make sure the website can load faster, when visited again. Another application is to track visitors to see how often they come and what they do. Then it becomes a marketing tool and you measure the behavior of visitors. Cookies can be adjusted, so they show which interests you have. If you visited a bicycle shop website, there is a chance that the advertisements on the next website that you visit is about bicycles which you can purchase.

Doctype: A doctype clarification shows which version of HTML is used in a document.
DNS: Stands for Domain Name Service: It converts IP-addresses into domain names. DNS-servers are equipped with an IP-address on your web server, that assigns your domain name to the servers. On the other hand, if somebody types in your domain name, the DNS servers translate that domain name into the IP-address and sends the browser to the correct web server.
Domain name: A domain is the address where you arrive when you visit a website. It is shown on the top of your browser and each domain name is unique. Your domain name is also assigned to a unique number, the so called IP number. The domain name of this site is wpjournalist.nl. You can make a .nl domain name extension, but also a foreign one, such as .be or .com. Today, more and more possibilities are available for domain name extensions, such as .amsterdam or .info.
Domain registration: You always need to register a domain name first. A domain name is usually only valid for one or two years, at the end of which it needs to be extended in order to remain useful. Often this happens automatically. You can register a domain name at your hosting provider.
Browsing: Looking through different kinds of websites on the internet.
Download: If you transfer information or files from a website or server to your computer, this is called downloading.
Embedding: The act of in-closing a video, infographic or other video content into a website. Youtube gives an embed code for example, with which you can paste a video in to your website. This can be done using the following code, for example:
E-mail: An email is a message which is sent from one computer to another instantly. Email is still one of the most important tools to communicate. You can send or receive an email, to just one person, or many.
E-mail client: Is the software program that you use for the sending and receiving of an email from your computer, tablet or smartphone. Outlook from windows is an example of an email client.
Favicon: The small (usually 16×16 pixels, although it can also be 32×32 pixels), pictogram that is shown in the web address bar. In most browsers, this is shown at the left side of the web address. They can be saved into a .ico, .gif or .png file format. The favicon is a recognition mark of a website, a small kind of logo.
![]()
Font: This is the font style that you use for your website, such as ‘serif’ or ‘sans-serif’. You can determine your own font for you website. Usually a theme already contains a couple of fonts, but you can also use Google fonts, for example, which you can use in your website for free, for example. Then you can choose between hundreds of different font types to make headlines, texts or quotes.
 Freeware: Software which is made available for free use. It is often used to tempt a user to purchase a paid version of that software. This paid version has more functions or is without advertisements.
Freeware: Software which is made available for free use. It is often used to tempt a user to purchase a paid version of that software. This paid version has more functions or is without advertisements.
FTP client: The software program that you use to upload your website to a host-server. An often-used ftp client is FileZilla.
GIF: A type of file which is used for images, in particular animated graphics and online drawn images. It is not often used for photos.
 Hexadecimal: A term to define colours online. Hexadecimal numbers are the numbers 0-9 and the letters A-F. The hexadecimal numbers are written in three sets of hex pairs. Because the screen colours are RGB (Red, green blue), the first pair defines the red hue, the second pair defines the green hue and the third pair defines the blue hue. You can easily work colours into your website. A red text is made as follows, for example:
Hexadecimal: A term to define colours online. Hexadecimal numbers are the numbers 0-9 and the letters A-F. The hexadecimal numbers are written in three sets of hex pairs. Because the screen colours are RGB (Red, green blue), the first pair defines the red hue, the second pair defines the green hue and the third pair defines the blue hue. You can easily work colours into your website. A red text is made as follows, for example:
<span style=”color: #ff0000;”>test</span>
The #ff0000 is the hexa code for the colour.
Hit: A hit on your website is essentially the request for a single file from your web server. This means that a visit to a page can generate multiple hits.
Hosting: You can let a hosting party host your website. They will take care of three things: An IP (domain) address, physical space to save the website and the traffic with other servers.
.htaccess: This file is important in the directory of your website. Within the .htaccess file, multiple things are arranged, such as authority, access to the website and security options. A small typing error in your .htaccess file will make your website completely inaccessible. Before you go on to change something, you should make a backup first.

HTML: Stands for Hyper Text Markup Language. This is the standard language for creating websites. Documents in HTML are read by a web browser to be shown as a web page afterwards. HTML-documents contain a semantic structure and textual content of a webpage in the first place. The layout and view of images can also be described, but usually another coding language is used for that: CSS.
HTML Element: With a HTML-element, you can make a word or text bold, italic or give it another appearance. If you want to make a word bold, you use b-tag. You do it like this: This part is bold
HTTPS: This means HyperText Transfer Protocol over SSL (Secure Socket Layer) or alternate HyperText Transfer Protocol Secure. This is the same as HTTP, but through a secured, encrypted connection.
IE: This stands for Internet Explorer. This is one of the most popular Internet Browsers by Windows.
IP-address: IP stands for Internet Protocol. It is an address with which a ‘network-map’ of a host in a network, can unambiguously be addressed within the TCP/IP-model, the standard of the internet. If you buy a subscription at a hosting party, you often get an IP-address, that connects you to a website.
ISP: Internet Service Provider, a company that takes care of the hosting of your website. This can be the connection with internet, but also services that the user can use through the internet.
Javascript: Is an emerging script language to make webpages interactive and develop web applications. The script is transmitted in a web browser with use of HTML and is carried out in here. In the future, WordPress will be fully switched over to Javascript, instead of the coding language CCS. An important development!
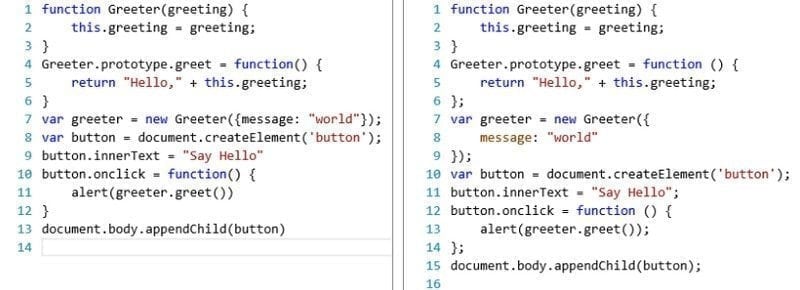
JPG: A type of file that is often used for images, in particular for pictures.
Keyword: The most important (key)word in an article. For Google, this is an important recognition point to know what the article is about. Therefore, it is important that you put keywords in your article, to be found by search engines in a better way.
LAN: Local Area Network. It is a small network of computers which are connected to each other. This way, you can exchange files between computers in an easier way.
Landing page: A landing page is the page where a visitor can ‘land’. A landing page is often used to promote a specific product or service, a book for example. The landing page often has no distraction, such as a navigation bar or a side-bar. Everything is focused on that one product.
Take a look at Unbounce for example, where you can easily create your own landing page.
Meta Description: This is the data in the header with information about the webpage which is offered to a visitor. The information in the meta data is not visible on the webpage (only in the source-code).
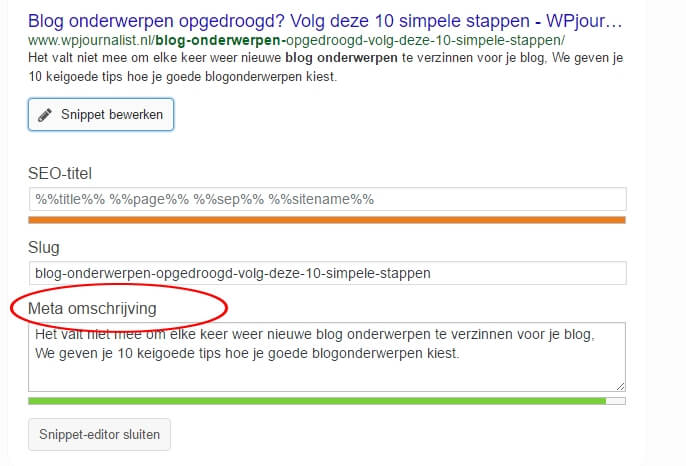
You can add Meta Data for every page or article. This can be done with the plugin SEO Yoast for example. This way, you can let Google know what the page or article is about.
Navigation: This is the structure of your website, an important part. Through the navigation, the visitor can be directed from one part of the website to another. If this is not good or clear, the visitor will leave quickly. Usually, on the top or at the left- or right side of a navigation bar or menu, with which the visitors can orientate themselves.
Open source: The production and development of tools and software which can be used freely for further development of software, or online products or services.
Pageview: Stands for the amount of times a page from a website is viewed. For every pageview you get, someone is looking at that page.
Pay per click: Is often used in the world of advertisements on the internet. Instead of paying a fixed monthly amount, you pay a small amount each time someone clicks on your banner or advertisement.
Permalink: This is the address of a certain blog post. In WordPress, you can set permalinks. This is usually set to ‘standard’, but it is better to adjust it to ‘message name’. In the address of your blogpost, you (and also search engines) will easier see what the article is about. Because instead of numbers, the headline of your article appears.
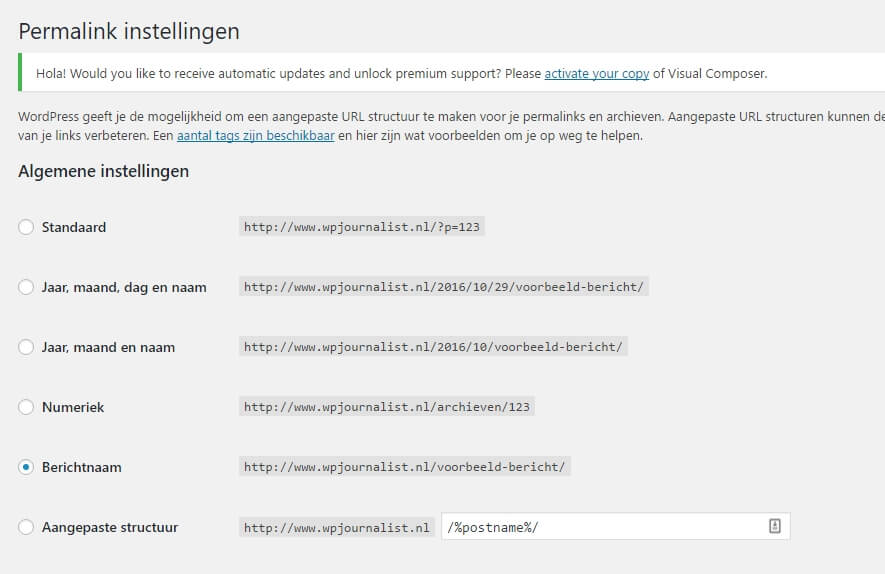
PHP: A program language that is set on Linux. It works in combination with html and ensures that functions are carried out from the server.
Plugin: To give more functionality to WordPress, you can use a plugin. It’s just like accessories with which you can pimp your car, such as an extra mirror or tinted windows. WordPress has a couple of standard functions, but there are plugins to make you website load faster, or to add a chat function, or turn it into a webshop. It is a piece of software that gives your website this new function. There are thousands of plugins that you can add to your website. An important overview can be seen in the Plugin Catalogue.
Root: The files which are necessary to build your own website, are saved on the server in different maps, arranged in a hierarchical order. The most important map in which all other maps and sub-maps for your account are stored, is called the head-map, also known as the root.
RSS: Stand for Really Simple Syndication. RSS makes it possible that visitors can subscribe to a blog and receive updates through a RSS-reader. The last couple of years, the popularity of the RSS is going down; less people are using it.
Search Engine: A program that collects information out of millions of websites and pages on the internet. Google is the most popular search engine, but there are many more, such as Yahoo or Bing. In the Netherlands there is the search engine called vinden.nl, but it is nowhere near as popular and known as for example Google.
Script: A piece of code with a specific function on a website. The user capabilities are endless, just like the different kinds of scripts that can be used, written in different languages, such as JavaScript.
Scroll: A page of a website that is often longer than what you can see on your computer or phone. If you go down to see more of the page, that is called scrolling.
SEO: An English term that stands for Search Engine Optimization. It is a collection of techniques, focused on the optimization of websites or internet pages for the search engines findability. For example Google, adds value to websites by using search engine ranking factors. These are factors such as the amount of words in a text, speed of your website and many more. An overview of all the factors can be found in the article Googles 200 ranking factors.

Server: A server is a computer that is used for the physical storage area for websites and e-mails. Without a server, your websites would not be visible. Servers are, in most cases, taken care of by hosting companies that keep the servers in special areas.
Shareware: Is a piece of software which you can use for free for a certain amount of time. After that period, you need to purchase it with a license fee, to be able to keep using that software.
SIDN: At the ‘Stichting Internet Domeinnaamregistratie Nederland’ (SIDN), you can check whether or not a domain name is already registered and by who.
Sitemap: This is an index for all the content on your website. The goal of this is to help people find what they are looking for on your site. But search engines can also clearly see the structure of your website this way. A good structure is rewarded with a higher position in the search results.
Spam: Spam is unwanted email, usually sent in large amounts and which you didn’t ask for. Spam is for example sent to convince you to buy something. Even worse is that there could be a virus in your spam-mail which can be a danger to your website.
Subdomain: A domain which is part of a normal domain, but can be operated completely independently. With WPjournalist, a subdomain could be http://help.wpjournalist.nl. You can see that the www is substituted by help. On this subdomain, you can install a separately working website.
Tag: Creates a different layout of your website. A website has a navigation or a menu, but it does not show the content from different perspectives. Tags do. Usually, tags are at the beginning or at the end of an article.
Template of theme: Is a ready-to-go website, including a content management system. Nowadays, you can buy a complete website for a small price, for example at Themeforest, a market place for websites. WPjournalist was for example also bought here and derives from Newspaper.

Trojan horse: A virus (evil code) which can infect your computer, so that malicious types can take over your computer or harm it in some way. Usually this happens when you open a file that is sent to you through email. But hackers can also break in through a weak password, a bad secured server or a unupdated WordPress.
Unique visitor: This term is often used to determine how many visitors come to your website. Each person that visits your website is a unique person.
Uploading: If you send information, pages, photo’s etc. to your website with a ftp-program, that is called uploading.
URL: Means Uniform Resource Locator. A URL is a unique web address. https://wpjournalist.nl for example is an URL.
Connection: You need this to get onto the internet. Usually you can arrange this through a hosting provider. You also need a link to arrange a connection through a cable- or telephone supplier. You have different kinds of connections: Cable, ADSL and wireless.
Webmail: The email box that you can check all around the world from any computer.
Webpage: One page from a website. A page is not the same as a message in WordPress. Pages are often a bit static and consist of fixed parts, such as ‘home’, ‘about us’, ‘services’, ‘portfolio’, ‘contact’ etc.
Website: The actual website itself. This contains the front (what the internet sees) as well as the back (the cms from which you can manage your website)
WWW: World Wide Web. Another name for the internet.

XML: Stands for Extensible Markup Language. You can download an XML document from your existing WordPress website for example. It holds all the pages, messages, images and comments. These can then be uploaded to your new site and this way you can easily exchange content from one website to another.
Search engine: A place where information about hundreds, thousands and millions of websites are being stored, so that people can easily and quickly find information.
Search results: When someone is looking for something by using a search engine, a list of websites appears in the search engine: the search results. The goal of a website is to appear as high as possible within the search results.




